In a remarkable development in the field of space technology, a Japanese startup based in Sapporo has created an innovative type of fuel made from plastic.
A Surprising Innovation in Space Fuel
This solid plastic fuel is designed to power small satellites and may soon be used to launch full-scale rockets. What makes this fuel unique is not just its composition, but also its safety, cost-effectiveness, and ease of handling.
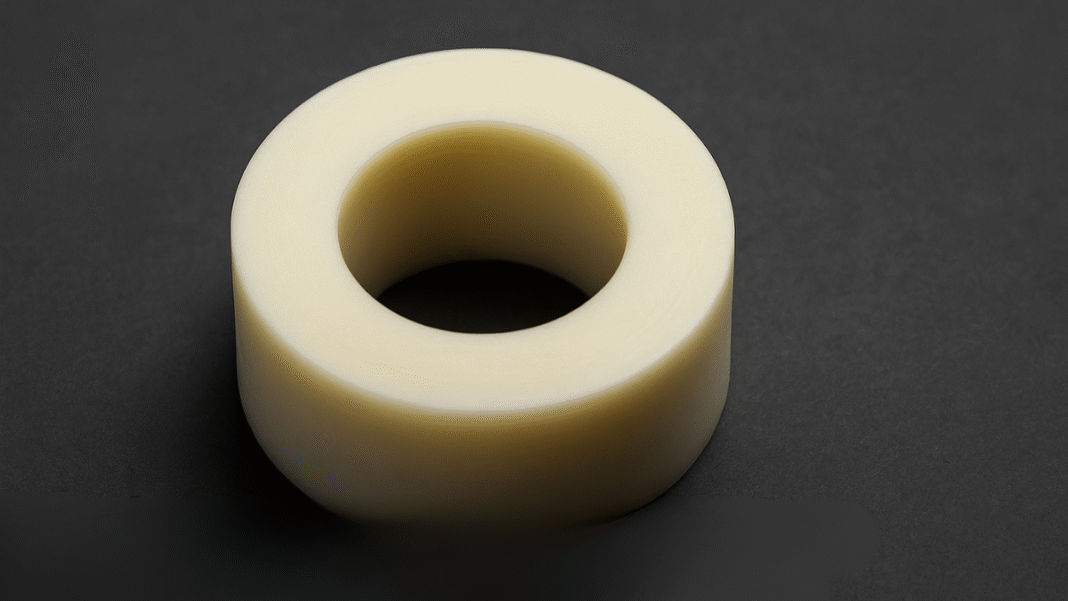
At first glance, the fuel looks like the empty ring you’re left with when a roll of tape runs out. But this unassuming spool-like structure is actually rocket fuel. Unlike the traditional liquid fuels used in rockets, which are highly combustible and require extreme care, this plastic-based fuel is much safer and easier to manage.
Traditional rocket fuels are known for their explosive nature. A minor mistake during storage or fueling can lead to major accidents, including the destruction of the entire satellite payload. In contrast, this new plastic fuel is stable enough to be carried in a pocket on a commercial flight — a clear indication of its low reactivity under normal conditions.
Space Propulsion: The Ultimate Challenges and Breakthroughs Powering Tomorrow’s Exploration
Plastic Fuel That Melts, Not Explodes
The plastic fuel is used in a hybrid propulsion system, where it is combined with nitrous oxide (also known as laughing gas) to create thrust. Unlike typical rocket fuels that burn rapidly and explosively, this solid plastic fuel melts from the inside — much like how a candle slowly melts when lit.
This design has already been proven in space missions. The fuel was used to power cubesats — small, lightweight satellites usually weighing around 2 kilograms. These satellites are commonly used for earth observation, communication, and scientific research. The company showcased both unused and spent fuel rings, highlighting how the fuel is consumed during use.
Fuel Tanks That Vanish? Israeli F-35I Adir Carried the Secret That Changed the Combat Gam
According to the startup, this new fuel system offers several key advantages:
- 70% lower costs compared to traditional fuels
- 50% reduction in leakage risks
- 30% less fuel mass, making it lighter for launch systems
The lower mass is especially important because every kilogram launched into space costs a significant amount of money. Using lighter fuel means more weight can be dedicated to satellite equipment or instruments, making each mission more productive.
This hybrid system is also cleaner and easier to maintain, with fewer moving parts and less risk of system failure. These features make it ideal for commercial space operations, which demand efficiency and cost control.
Moving Toward Full-Scale Rocket Launches
With successful space trials already completed, the startup now aims to expand the use of its fuel system to power full-size rockets. The company’s CAMUI rocket engine, which runs on this hybrid plastic fuel, is currently being prepared for test launches.
The company states that the engine could provide:
- 200% faster time to launch
- 60% lower overall launch costs
- Zero explosion risk during transport, storage, or fueling
These claims are backed by internal data and fact sheets displayed at the recent DSEI Japan trade show, where the company was featured alongside major aerospace firms. If successful, this could mark the first time in history that a full-scale rocket is launched using solid plastic fuel.
Geostationary Gamble: China’s Shijian-25 Aims to Refuel a Decommissioned Satellite in Orbit
Support for this innovation comes from notable investors, including All Nippon Airways Trading Co. Ltd., which showcased the fuel technology in its booth during the trade show. Their partnership helps highlight the growing interest in alternative, safe, and cost-effective fuel technologies for space missions.
This new fuel system not only promises to make space travel safer and more affordable but also opens up new possibilities for handling and transporting rocket fuel in a way that avoids the dangers traditionally associated with such missions.